Dennis Odijk
Publications on Geodesy 52, Delft, 2002. 262 pagina's.
ISBN-13: 978 90 6132 278 8. ISBN-10: 90 6123 278 2.
Summary
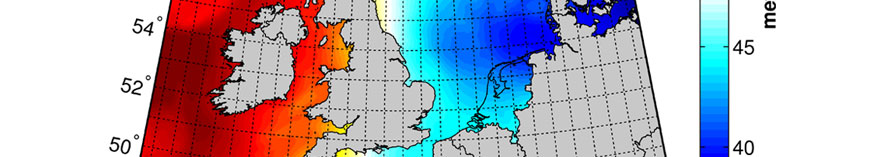
In many geodetic (surveying) applications positions of objects need to be determined with high precision (cm-accuracy or even better). The Global Positioning System (GPS) is very suitable for this purpose. High positioning accuracy is in principle feasible when a relative measurement setup is used and in the processing of GPS observations certain systematic errors are properly taken into account. The largest of these errors is due to the propagation of the GPS signals through the ionosphere, the part of the atmosphere from about 80 km altitude. When the distance between the GPS receivers in the relative measurement setup is sufficiently short (e.g. a few km) it is known that these errors almost cancel, such that the positioning can be conducted using a short time span of measurements, which is very favorable from an economical point of view. For longer distances the necessary time span increases enormously since unknown parameters for among others the ionospheric errors need to be estimated in the processing. In this thesis a procedure is outlined for the processing of relative GPS observations over medium distances (max. 50 km), while at the same time it should allow a user a short time span of measurements. An important requirement to this procedure is the availability of a permanent network of GPS reference stations in the vicinity of a user. From the observations this permanent network collects, it is possible to generate information about the ionospheric delays, which a user can consequently apply to correct his own GPS observations. Much attention in the thesis is paid to the mathematical modeling aspects of this procedure.
Contents
- Abstract
- Samenvatting
- Curriculum vitae
- Acknowledgements
- Introduction
- Setting up the precise relative GPS model
- Procedure for solving the GPS model
- The ionospheric error in GPS observations
- The ionosphere-weighted GPS model
- Fast GPS positioning using ionospheric information
- Conclusions and recommendations
- Bibliography
App. A. The Kronecker product
App. B. Undifferenced - double-differenced models
App. C. Adjustment and testing procedure in GPSveQ
App. D. Computation of some receiver/satellite-dependent matrices
App. E. Ionospheric delay time series as stochastic process
Samenvatting
Snelle precieze GPS-puntsbepaling in de aanwezigheid van ionosferische vertragingen
In veel geodetische (landmeetkundige) toepassingen moeten posities van objecten worden bepaald met een zeer hoge precisie (cm-niveau of zelfs beter). Het Global Positioning System (GPS) is uitermate geschikt voor dit doel. Puntsbepaling met hoge precisie is in principe haalbaar indien een relatieve meetopzet wordt gebruikt en in de verwerking van de GPS-metingen met bepaalde (systematische) fouten rekening wordt gehouden. De grootste van deze fouten ontstaat vanwege de voortplanting van de GPS-signalen door de ionosfeer, het gedeelte van de atmosfeer boven ongeveer 80 km hoogte. Wanneer de afstand tussen de GPS-ontvangers in de relatieve meetopzet voldoende kort is (bijv. een paar km), dan is het bekend dat deze fouten zichzelf nagenoeg opheffen, zodat de puntsbepaling kan worden gebaseerd op een korte tijdspanne van metingen, wat vanuit economisch perspectief erg gunstig is. Voor langere afstanden neemt de noodzakelijke tijdspanne enorm toe, omdat onbekende parameters voor o.a. de ionosferische fouten moeten worden geschat in de verwerking. In dit proefschrift wordt een procedure uiteengezet voor de verwerking van relatieve GPS-metingen over middelbare afstanden (max. 50 km), welke tegelijkertijd een korte meettijd zou moeten toestaan voor een gebruiker. Een belangrijk vereiste t.a.v. deze procedure is de beschikbaarheid van een permanent netwerk van GPS-referentiestations in de omgeving van de gebruiker. Uit de waarnemingen die dit permanent netwerk verzamelt is het mogelijk om onder meer informatie over de ionosferische vertragingen te genereren, welke de gebruiker vervolgens kan toepassen om zijn eigen GPS-metingen te corrigeren. In het proefschrift wordt veel aandacht geschonken aan de wiskundige modelleringsaspecten van zo'n procedure.